Enterprise Risk Management
What is ERM?
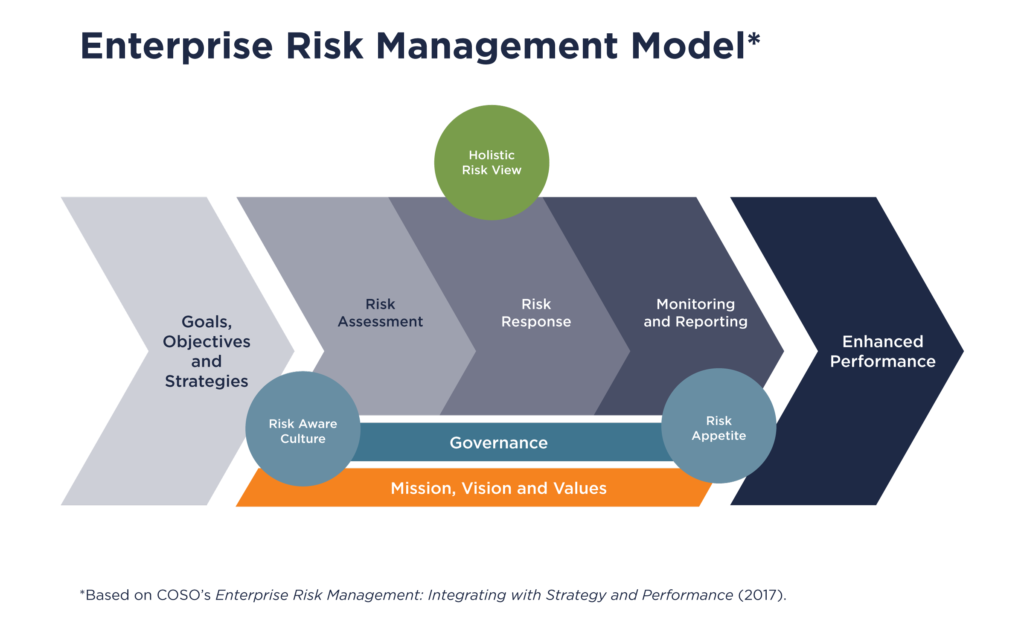
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is an approach an organization’s leaders use to develop (1) a holistic view of all types of risks related to achieving goals and objectives and (2) appropriate responses to those risks. Risks can be positive (an opportunity) or negative (a threat). The goal of using ERM is to improve decision-making, leading to improved performance.
Leaders use ERM when developing strategy, conducting operations, managing finances and ensuring compliance. For optimal effect, ERM can be integrated with existing organizational processes, such as strategic planning, budgeting and performance measurement.
What is a Risk?
A risk is a potential event (an uncertainty) that may impact an organization’s ability to achieve its goals and objectives. The impacts can be positive, presenting an opportunity, or negative, presenting a threat. Managing uncertainty is a key responsibility of an organization’s leaders.
UT’s ERM Initiative
All state agencies, including the University of Tennessee, are required by state statute—the Financial Integrity Act of 1983—to perform an annual “assessment of risks,” among other activities. The Tennessee Department of Finance and Administration (F&A) is charged with developing implementation guidelines.
These guidelines require agencies to implement ERM in alignment with the Committee of Sponsoring Organization’s (COSO) ERM framework: Enterprise Risk Management—Aligning Risk with Strategy and Performance (2017). UT’s approach is based on that framework but is tailored to fit the needs of a higher education institution.
Though the statutory requirement was the impetus for the initiative, creating a “risk aware” culture thought the implementation of ERM will benefit the university by providing leaders at all levels with methods to manage the uncertainties that must be addressed in pursuit of goals and objectives.
ERM Benefits
- A holistic perspective of risks across the entire institution, leading to better priority setting and resource allocation.
- A deeper understanding of the uncertainties facing the university, its ability to address those uncertainties and the alternatives for responding.
- A consistent methodology and language to use across all segments of the institution which can improve communication about goals, objectives and strategies.
- Documented assurances for stakeholders that the university is appropriately addressing risk.