UT’s ERM Process
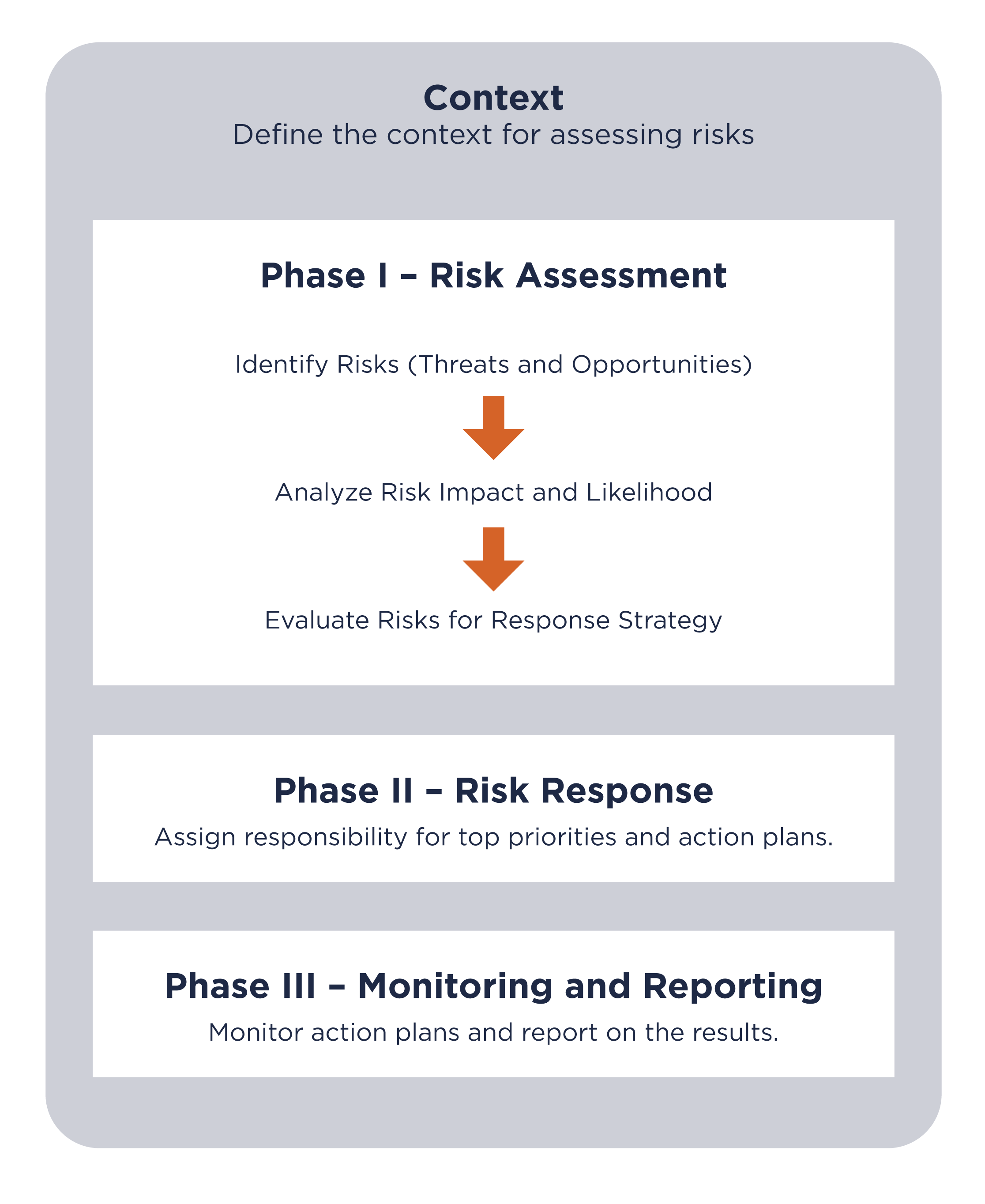
UT’s ERM process involves three phases: Phase I Risk Assessment, Phase II Risk Response and Phase III Monitoring and Reporting Results. To begin the process, the context within which risks will be addressed must be defined—e.g., the entire organization, a component unit or a proposed strategic initiative. In 2022, the focus of ERM activities is on the achievement of goals and objectives in the UT Systemwide Strategic Plan for 2021-2025. Once the context is clear, the risk assessment can begin.
Phase I Risk Assessment contains three activities: First, is to identify risks that could affect the achievement of goals and objectives—either negatively (threats) or positively (opportunities). The second is to analyze risk impact and the likelihood to determine the critical few threats and opportunities. For each threat and opportunity, the magnitude of the impact to the achievement of goals and objectives is determined and the likelihood of occurrence is assessed. The third activity is to evaluate risks for the appropriate response strategy. After considering the effectiveness of any current actions related to each threat or opportunity, a response strategy is determined. The strategies range from doing nothing (staying the current course) to creating action plans to mitigate a threat or pursue an opportunity.
Phase II Risk Response includes two activities: First, is that leaders must assign responsibility for responding to each threat and opportunity that requires a response. Identifying the appropriate position or office to address the risks requires leaders to consider who has the requisite knowledge, skills, abilities and scope of influence. Second, after responsibility has been assigned, leaders must request action plans and then review them to ensure key threats and opportunities are being addressed appropriately.
Phase III Monitoring and Reporting Results consists of two activities: First, monitoring the implementation of response plans and second, ensuring results of the plans are reported. Leaders and those responsible for implementing action plans collaborate to determine monitoring methods, the information to be collected, who performs tasks and when and how to document. This discussion also includes determining which stakeholders need to be informed and how often.

